Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs), also known as neutrophils, are white blood cells that play a crucial role in the immune response. They are the most abundant type of white blood cell in the human body, making up approximately 60-70% of all circulating leukocytes. PMNs are an essential component of the innate immune system, the body’s first line of defense against infection.
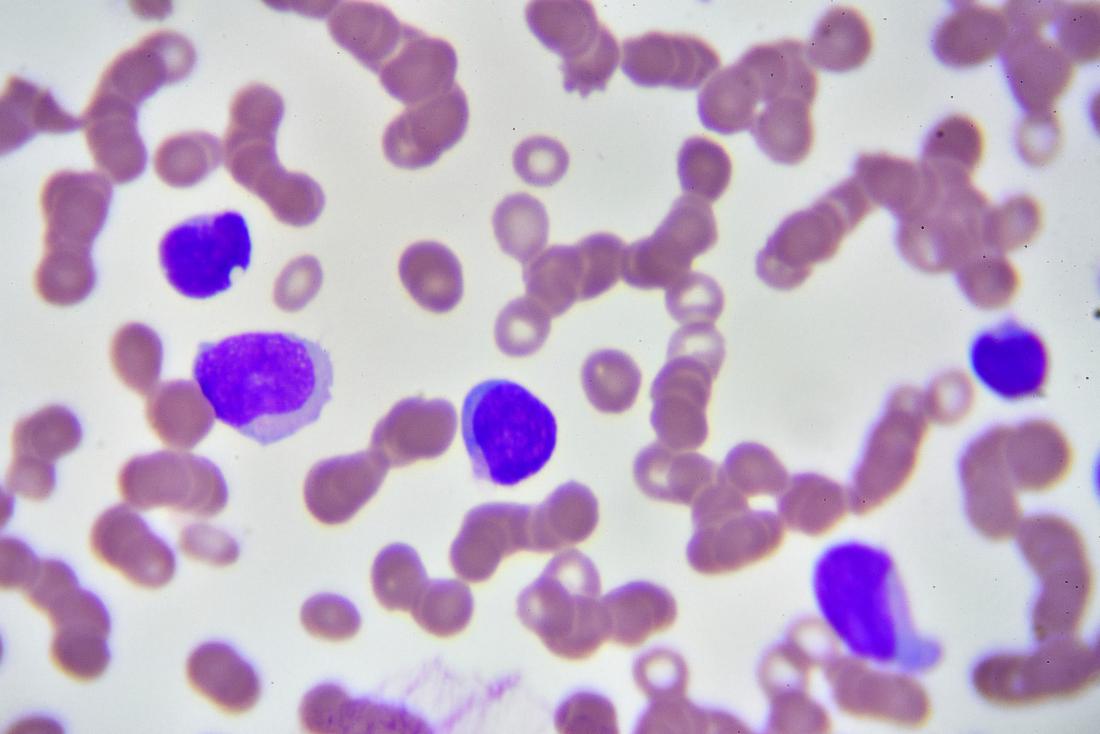
The Anatomy and Physiology of PMNs: Understanding their Structure and Function
PMNs have a unique structure that allows them to carry out their functions effectively. They are characterized by a multi-lobed nucleus called “polymorphonuclear.” This multi-lobed nucleus will enable PMNs to squeeze through narrow spaces and migrate to sites of infection or inflammation.
The main function of PMNs is to engulf and destroy pathogens through phagocytosis. They have specialized receptors on their surface that recognize and bind to foreign invaders, such as bacteria or fungi. Once attached, PMNs release toxic substances, such as reactive oxygen species and antimicrobial peptides, to kill the pathogens.
PMNs and their Role in Innate Immunity: The First Line of Defense Against Infection
Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense against infection. It is a non-specific immune response that provides immediate protection against various pathogens. PMNs play a crucial role in innate immunity by rapidly responding to disease or tissue damage.
When an infection occurs, PMNs are recruited to the site of disease through a process called chemotaxis. They are attracted by chemical signals released by damaged tissues or by other immune cells. Once at the site of infection, PMNs use their phagocytic abilities to engulf and destroy the pathogens.
PMNs and their Interaction with Other Immune Cells: A Complex Network of Defense
PMNs do not work alone in the immune response. They interact with other immune cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, to form a complex defense network. This network allows for a coordinated and efficient immune response.
PMNs can communicate with other immune cells by releasing chemical signals, such as cytokines and chemokines. These signals help recruit and activate other immune cells at the site of infection or inflammation. PMNs can also interact directly with other immune cells through cell-to-cell contact.
The importance of this complex network of defense is evident in the immune response to infections. When one type of immune cell cannot effectively eliminate a pathogen, other immune cells can provide additional support.
PMNs and Inflammatory Response: The Double-Edged Sword of Immune Defense
Inflammation is a crucial part of the immune response. It is a protective mechanism that helps eliminate pathogens and repair damaged tissues. PMNs play a significant role in the inflammatory response but can also be a double-edged sword.
When PMNs are activated, they release inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, which attract other immune cells to the site of infection or inflammation. This increases blood flow to the area, resulting in redness and swelling.
While inflammation is essential for fighting infections, excessive or prolonged inflammation can harm the body. It can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the development of chronic diseases, such as arthritis or cardiovascular disease.
PMNs and their Role in Wound Healing: The Healing Power of Immune Cells
Wound healing is a complex process involving various stages, including inflammation, tissue formation, and remodeling. PMNs play a crucial role in the early stages of wound healing, particularly in the inflammatory phase.
PMNs are among the first immune cells to arrive at the site when a wound occurs. They help remove debris and dead cells and release growth factors that promote tissue repair. Additionally, PMNs also release antimicrobial peptides to prevent infection in the wound.
However, excessive or prolonged presence of PMNs can delay the healing process. The body needs to regulate the recruitment and activation of PMNs to ensure proper wound healing.
PMNs and Their Role in Autoimmune Diseases: The Dark Side of Immune Response
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues. PMNs have been implicated in the development and progression of autoimmune diseases.
PMNs can activate and release inflammatory mediators in autoimmune diseases contributing to tissue damage. PMNs can also form immune complexes with antibodies, leading to inflammation and tissue destruction.
Understanding the role of PMNs in autoimmune diseases is crucial for developing targeted therapies that can modulate their function and reduce tissue damage.
PMNs and their Role in Cancer: The Battle Between Immune Cells and Tumor Cells
Cancer is a complex disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and invasion of healthy tissues. The immune system plays a critical role in recognizing and eliminating tumor cells. PMNs are key players in the battle against tumor cells.
PMNs can recognize tumor cells as foreign or abnormal and initiate an immune response against them. They can release cytotoxic substances that directly kill tumor cells or recruit other immune cells to attack the tumor.
However, tumor cells have developed various mechanisms to evade immune recognition and destruction. They can produce factors that suppress the function of PMNs or recruit immunosuppressive cells that inhibit the immune response.
Understanding the interaction between PMNs and tumor cells is essential for developing effective cancer therapies that harness the immune system’s power to fight cancer.
PMNs and their Role in Immunotherapy: Harnessing the Power of Immune Cells for Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy is a promising approach to cancer treatment that aims to enhance the body’s immune response against tumor cells. PMNs have emerged as potential targets for immunotherapy due to their ability to recognize and eliminate tumor cells.
Several strategies are being explored to harness the power of PMNs for cancer treatment. These include enhancing their function, modulating their recruitment to the tumor site, or using genetically modified PMNs to target tumor cells specifically.
Immunotherapy has shown promising results in some cancer types, but further research is needed to optimize its effectiveness and minimize side effects.
Future Directions in PMN Research: Unlocking the Potential of Immune Cells for Therapeutic Applications
Research on PMNs is ongoing, and many unanswered questions remain about their function and potential therapeutic applications. Future directions in PMN research include understanding the mechanisms regulating their recruitment and activation, identifying new targets for immunotherapy, and developing novel therapies to modulate their function.
The potential therapeutic applications of PMNs extend beyond cancer treatment. They could also target other diseases, such as autoimmune diseases or chronic inflammatory conditions.
In conclusion, polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are crucial in the immune response. They are the first line of defense against infection. They interact with other immune cells to form a complex defense network and contribute to various aspects of immune function, including wound healing and cancer surveillance. Understanding the anatomy, physiology, and part of PMNs is essential for developing targeted therapies that can modulate their position and improve immune responses in various diseases.
 Fit Netion My WordPress Blog
Fit Netion My WordPress Blog



